Relief of Foreign - Body Airway Obstruction
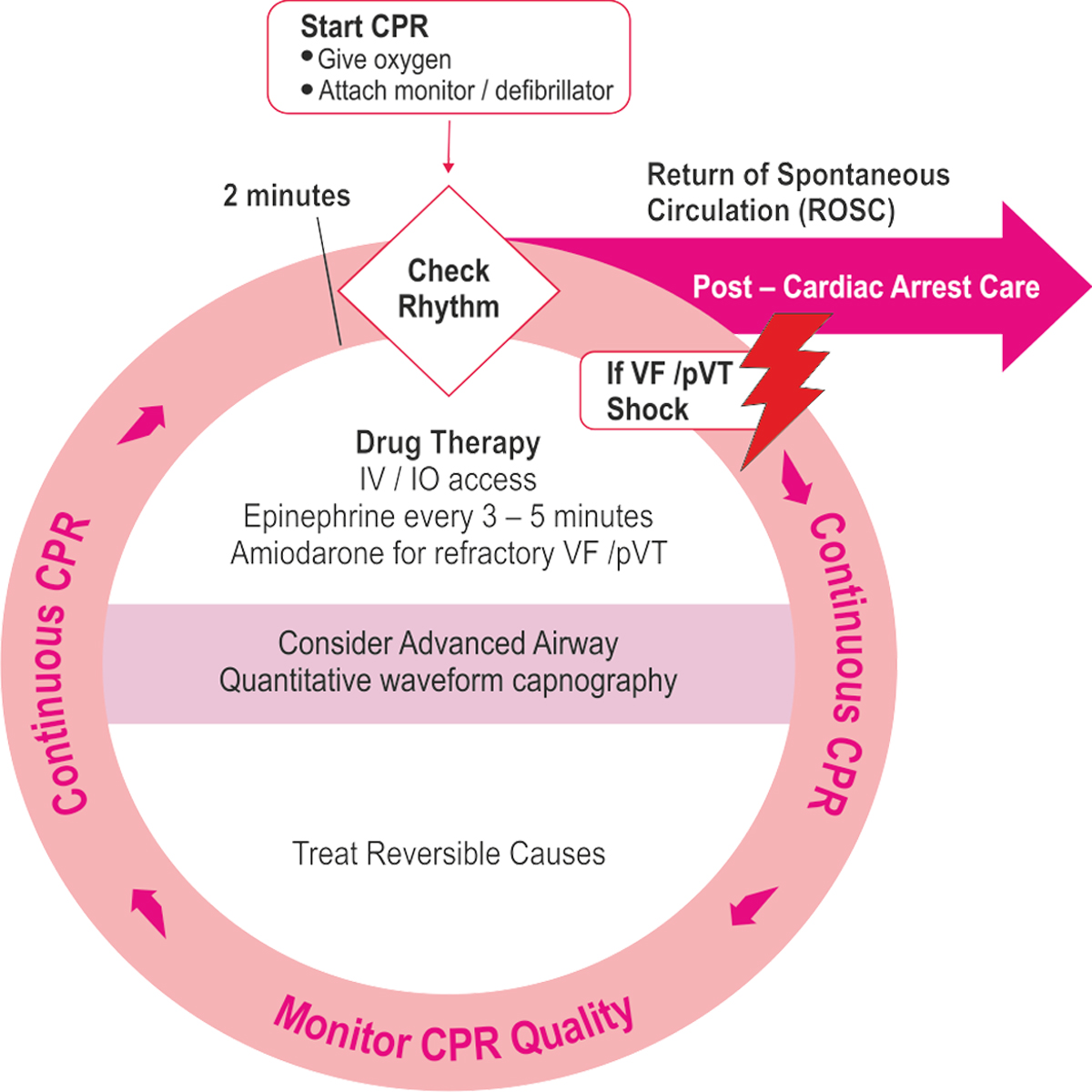
Cardiac Arrest Algorithm - 2015 Update
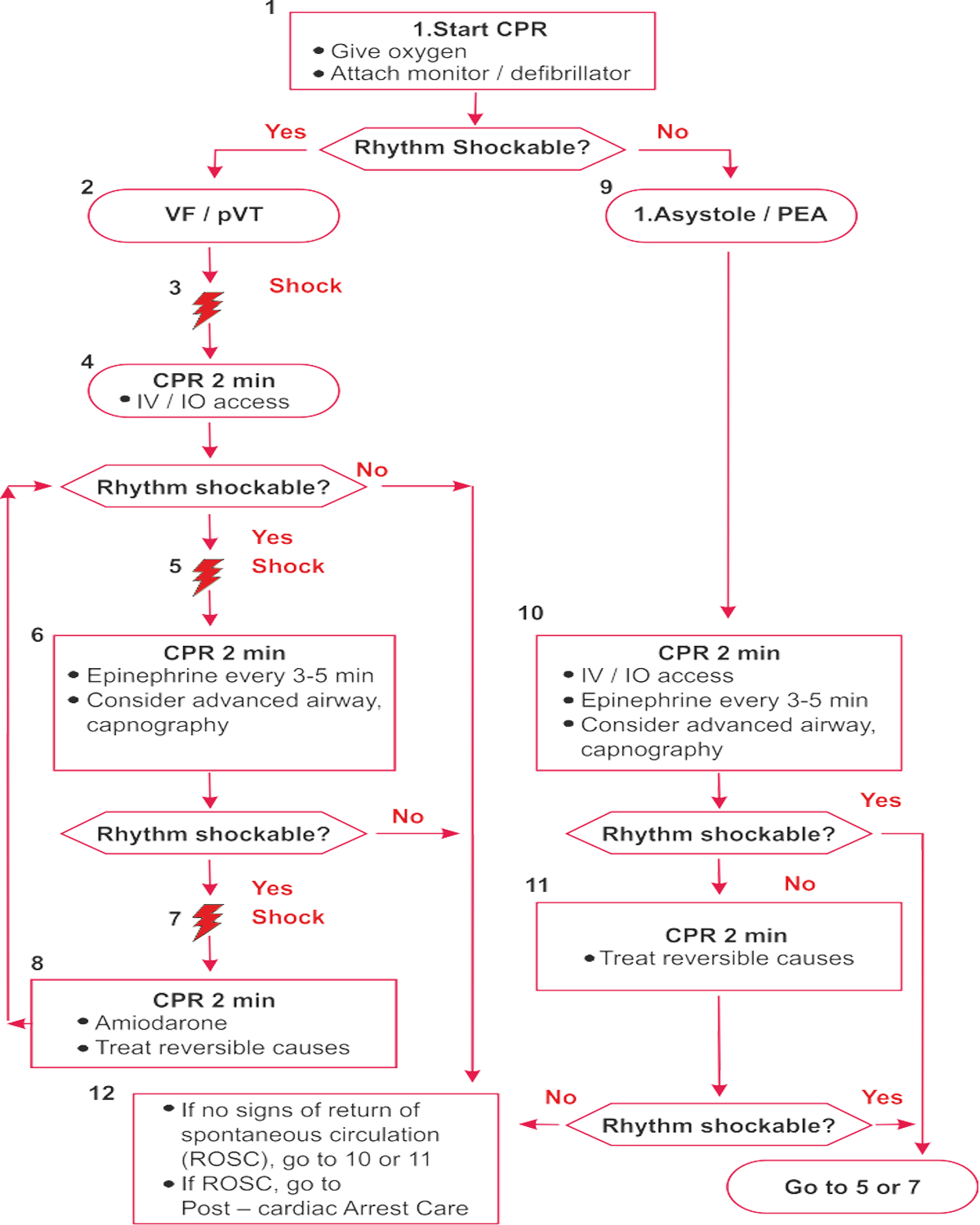
Key Points
CPR Quality
- Push hard (at least 5 om) and fast (100 — 120/min) and allow complete chest recoil
- Minimize interruptions in compressions
- Avoid excessive ventilation
- Rotate compressor every 2 minute, or sooner if fatigues
- If no advanced airway, 30:2 compression- ventilation ratio
- Quantitative waveform capnography — If PETCOi< 20mmHsg, attempt to improve CPR quality Intra-arterial pressure
– Ifrelaxation phase (diastolic) pressure <20mm Hg, attempt to improve CPR quality.
Advanced Airway
- Endotracheal intubation or supraglottic advanced airway
- Waveform capnography or capnometry to confirm and monitor ET tube placement
- Once advanced airway in place, give 1 breath every 6 seconds (10 breaths / min) with continuous chest compressions
Shock Energy for Defibrillation
- Biphasic: Manufacturer recommendation (eg: intial dose of 120-200J); if unknown, use maximum available
- Second and subsequent doses should be equivalent, and higher doses may be considered
- Monophasic: 360J
Drug Therapy
- Epinephrine IVIIO dose: 1 mg every 3-5 minutes
- Amiodarone IV/IO dose: First dose: 300mg bolus Second dose: 150mg
Return of Spontaneous Circulation(ROSC)
- Pulse and blood pressure
- Abrupt sustained increase in PETCO) (typically 240mmHg)
- Spontaneous arterial pressure waves with intra-arterial monitoring
Reversible Causes
- Hypovolemia * Hypoxia * Hydrogen ion (acidosis) * Hypo-/hyperkalemiaHypothermia
- Tension pneumothorax * Tamponade, cardiac * Toxins Thrombosis, pulmonary
- Thrombosis, coronary
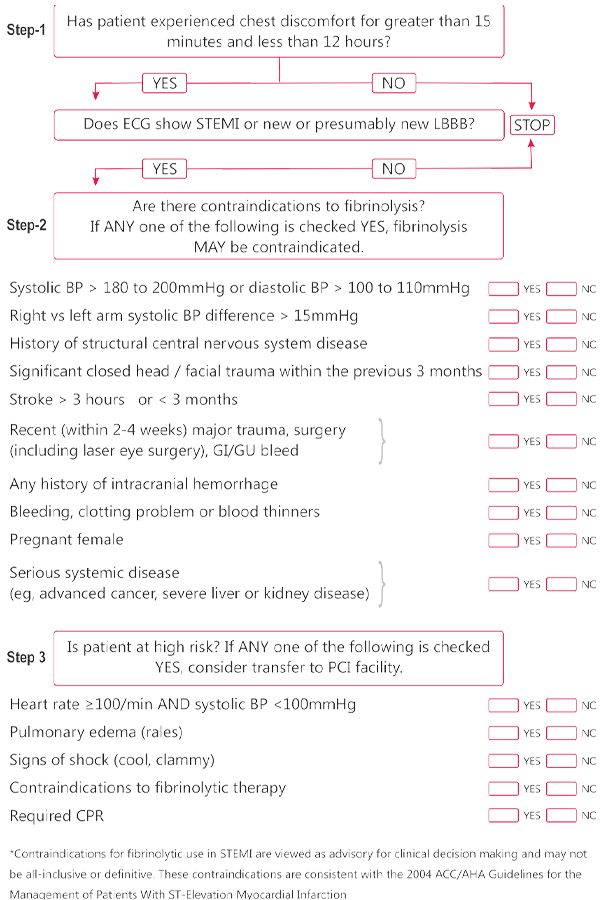
Fibrinolytic Therapy for STEMI
Contraindications for fibrinolytic use in STEMI consistent with ACC/AHA 2007 Focused Update*
Absolute Contraindications
- Any prior intracranial hemorrhage
- Known structural cerebral vascular lesion (eg, arteriovenous malformation)
- Known malignant intracranial neoplasm (primary or metastatic)
- Ischemic stroke within 3 months EXCEPT acute ischemic stroke within 3 hours
- Suspected aortic dissection
- Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis (excluding menses)
- Significant closed head trauma or facial trauma within 3 months
Relative Contraindications
- History of chronic, severe, poorly controlled hypertension
- Severe uncontrolled hypertension on presentation
- (SBP >180mmHg or DBP >110mmHg)+
- History of prior ischemic stroke > 3months, dementia or known intracranial pathology not covered in contraindications
- Traumatic or prolonged (>10 minutes) CPR or major surgery (s 3 weeks)
- Recent (within 2 to 4 weeks) internal bleeding
- Non-compressible vascular punctures
For streptokinase / anistreplase:
- Prior exposure (>5 days ago) or prior allergic reaction to these agents
- Pregnancy
- Active peptic ulcer
- Current use of anticoagulants: the higher the INR, the higher the risk of bleeding

